Published and edited by: Cheng Yu
WUST News - The ONTOWEB research team from the School of Computer Science and Technology at Wuhan University of Science and Technology (WUST), in collaboration with Prof. Daniel Hershcovich (University of Copenhagen) and Prof. Wu Xun (The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Guangzhou), has achieved a series of important advances in the field of artificial intelligence and cultural value alignment. Focusing on the core challenge of enabling large language models to accurately understand and respect diverse cultural values, the team has produced three high-quality papers accepted at top-tier international venues: NAACL 2025, EMNLP 2025 (CCF Class B), and Elsevier’s journal Information Processing & Management (IP&M, SCI Q1, CCF Class B). The team has also released corresponding code and datasets to the global academic community. These achievements were supported by the "Tech for Social Good: Driving Social Impact" Global Development Research Program, co-organized by the National University of Singapore and Tencent.
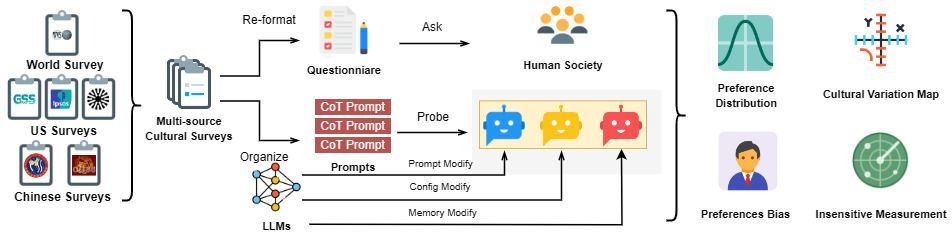
Figure 1: Evaluation System Flowchart
In their first study, the team addressed scientific limitations in existing evaluation systems for cultural value alignment. They found that existing cultural value alignment assessments often overlook the lack of diversity in large model outputs under contextual disturbances, which may potentially lead to distorted conclusions. To tackle this, the study proposed a Diversity Enhancement Framework (DEF), (Figure 1), which amplifies potential differences and quantifies their impact through three mechanisms: city-level context sampling, random truncation of memory length, and decoding parameter perturbation. Comprehensive experiments based on 1,153 mainstream social survey questions from China and the United States indicated that DEF enhances the diversity of model responses by nearly 90%, and for the first time, revealed gender and age preference biases at the system level, providing an operational benchmark for subsequent fairness improvements.
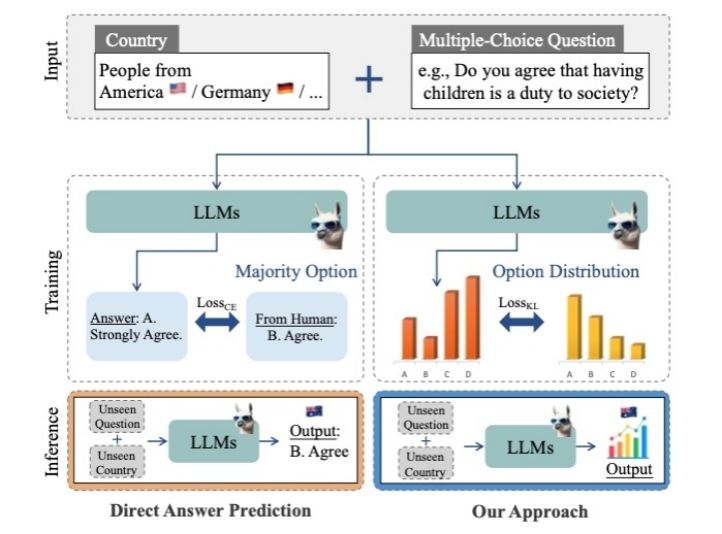
Figure 2: First-Word Probability Distribution Alignment Fine-Tuning Method
The second study aimed to overcome the high cost and long duration associated with global value surveys. The team introduced a fine-tuning method based on first-word probability distribution alignment (Figure 2), enabling large models to simulate human-like response distributions for countries and questionnaires lacking field data.
The experiment covered 65 countries and 259 questions from the World Values Survey (2017–2022), demonstrating that this method can significantly reduce prediction errors and maintain robustness on completely unseen questions and national contexts, offering a transferable and scalable new paradigm for cross-cultural social research.
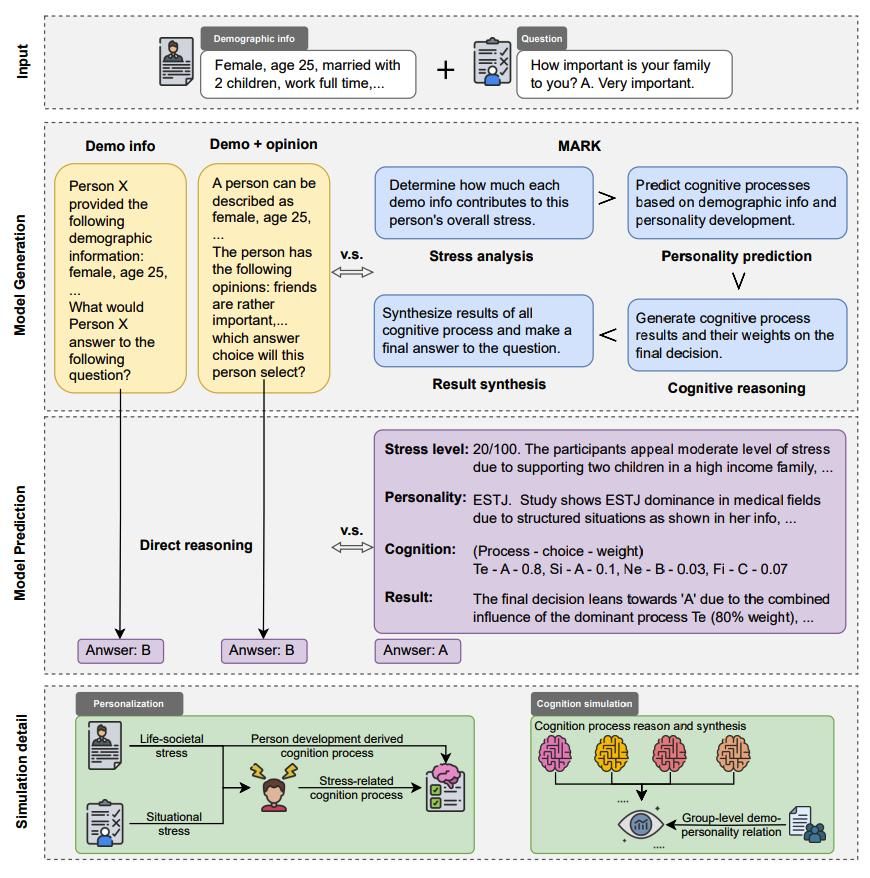
Figure 3: Multi-stage Cognitive Reasoning Framework MARK
In the third study, the team shifted the research perspective from macro groups to micro individuals, systematically reflecting on the stereotype risks that traditional "demographic label" prompt strategies might pose. Drawing on theories from personality psychology, the team developed a multi-stage cognitive reasoning framework called MARK (Figure 3). This framework first evaluates individual situational stress, then infers cognitive function preferences, and simulates the dynamic interaction of different psychological processes in questionnaire responses, ultimately producing answers that are both explanatory and accurate. Experiments on a bi-cultural dataset from China and the United States showed that this framework can improve prediction accuracy by approximately ten percentage points while significantly reducing the model's mechanical reliance on explicit features such as gender and age.
These three studies build progressively, forming a complete research loop from "evaluation method introspection" to "macro distribution simulation" to "micro psychological modeling," marking a substantial advance in WUST’s interdisciplinary integration of AI and social sciences. The ONTOWEB team remains committed to the principles of rigor, openness, and sharing, further deepening theoretical and technical work in cultural value alignment for large models, and contributing WUST’s expertise to global digital humanities and national digital governance.